Last time, we introduced the concept of duplication. It's a powerful idea, one of the crucial tactical ideas in backgammon. Look for your opponent's numbers that already play well, and remember that plays which expose blots to those very same numbers elsewhere on the board become stronger than they at first appear.
Last time, we introduced the concept of duplication. It's a powerful idea, one of the crucial tactical ideas in backgammon. Look for your opponent's numbers that already play well, and remember that plays which expose blots to those very same numbers elsewhere on the board become stronger than they at first appear.
The basic idea is pretty simple. You want to minimize the number of his rolls that can hurt you.
Here's another cute example.
|
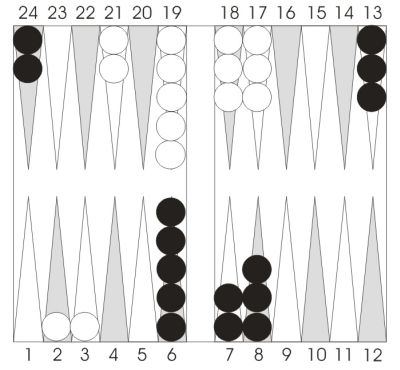
Position 1.
Black to play 6-1.
|
Black's not crushed yet in Position 1. but his game is starting to slide downhill. His back men haven't moved yet, and White has a ton of attackers in play in case Black decides to split. Up front, he's made his bar-point, but have a lot of numbers to extend his little prime. Meanwhile, White's checkers are poised to escape, and he's got a nice diversification, with small numbers building his 5-point, and large numbers hopping into Black's outfield.
At first, 61 doesn't look like a particularly good shot for Black. Splitting in back with 24/23, 13/7 isn't inviting. White's few remaining awkward numbers, like 66, 55, and 44, now become crushers, while everything else continues to play well. 13/7, 13/12 looks constructive, but contains a subtle flaw. It's not the immediate danger—only 63 and 64 hit for White. But if White hops into the outfield next turn without hitting—61, 62, 51, and 53, for instance —Black has to deal with this blot rather than build his board. The longer Black goes with building his board, the more danger he faces. The simple 13/7, 8/7 eliminates the outfield danger, at the cost of leaving even fewer point-making numbers.
The solution is hard to find: it's 13/7, 6/5! Slotting into a double shot is a rare play. Circumstances have to be just right, and here they are. First, there's some duplication involved. The small number combinations now give White the choice of hitting or making the 5-point. He will choose to hit, but it's only clear with the 32 roll. With 21 and 31, hitting gets the nod only because of the extra gammon chances generated by a third man back. (At double match point, White should build his 5-prime with these two rolls.) As for the other hitting numbers, Black is worse off for having slotted, but not by much. White still only has a 2-point board, and Black's checkers are suddenly well-developed and in play. And of course if White misses altogether, Black is delighted. After some rolls like 55 and 44, Black is already the favorite, while mediocre rolls like 54 and 41 leave the game even money!
Backgammon is a tough game because a long series of completely routine and easy plays can be punctuated by the need to make a sudden, crucial and decisive play. Get it right, and the game can lurch quickly in your direction. Get it wrong, and the game will slip away from you.
Next time: Hit or No Hit?
|

![]()